The Types of Chemical Reactions Packet delves into the fascinating world of chemical transformations, unraveling the intricacies of various reaction mechanisms and their significance in shaping our world. From the synthesis of life-sustaining molecules to the combustion of fuels, chemical reactions underpin countless processes that define our existence.
This comprehensive guide provides a structured exploration of the different types of chemical reactions, their classification, applications, and the factors that govern their behavior. Through engaging explanations, illustrative examples, and practical insights, we aim to illuminate the fundamental principles that drive chemical reactivity and its profound impact on our lives.
1. Types of Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions are processes that involve the rearrangement of atoms or molecules to form new substances. There are several types of chemical reactions, each with its own characteristics and mechanisms.
The main types of chemical reactions include:
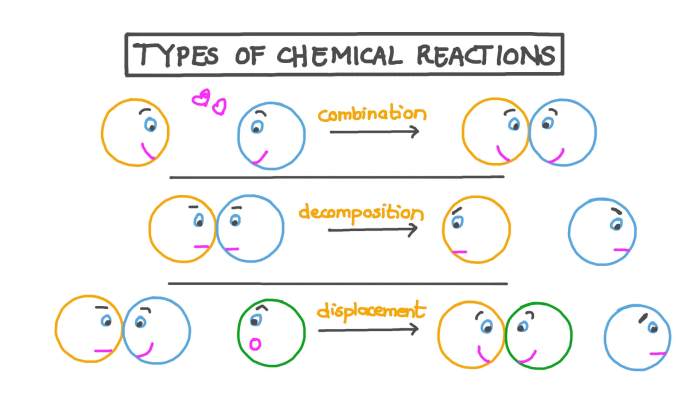
- Combination reactions
- Decomposition reactions
- Single-replacement reactions
- Double-replacement reactions
- Combustion reactions
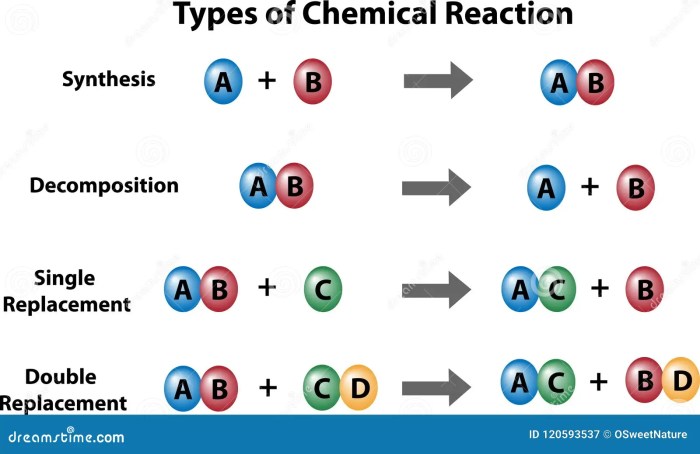
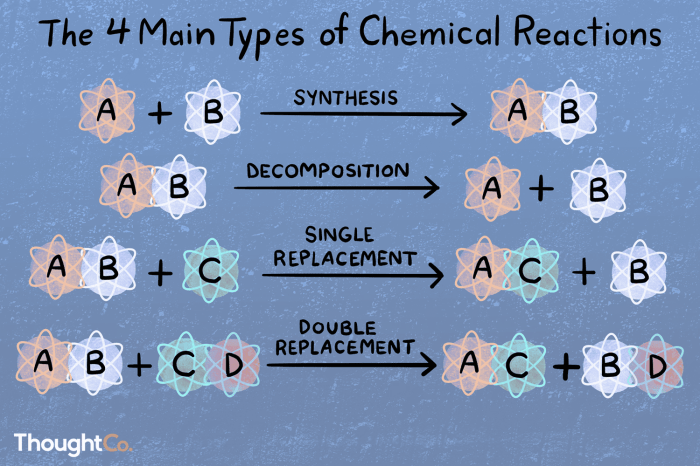
Combination Reactions, Types of chemical reactions packet
Combination reactions, also known as synthesis reactions, occur when two or more substances combine to form a single, more complex substance. The general equation for a combination reaction is:
A + B → AB
For example, when hydrogen gas (H 2) and oxygen gas (O 2) combine, they form water (H 2O).
Decomposition Reactions
Decomposition reactions are the opposite of combination reactions. They occur when a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. The general equation for a decomposition reaction is:
AB → A + B
For example, when water (H 2O) is heated, it breaks down into hydrogen gas (H 2) and oxygen gas (O 2).
Single-Replacement Reactions
Single-replacement reactions occur when an element replaces another element in a compound. The general equation for a single-replacement reaction is:
A + BC → AC + B
For example, when iron (Fe) is placed in a solution of copper sulfate (CuSO 4), the iron replaces the copper in the compound, forming iron sulfate (FeSO 4) and copper metal (Cu).
Double-Replacement Reactions
Double-replacement reactions occur when two compounds exchange ions to form two new compounds. The general equation for a double-replacement reaction is:
AB + CD → AD + CB
For example, when sodium chloride (NaCl) is added to a solution of silver nitrate (AgNO 3), the sodium ions (Na +) replace the silver ions (Ag +) in the compound, forming sodium nitrate (NaNO 3) and silver chloride (AgCl).
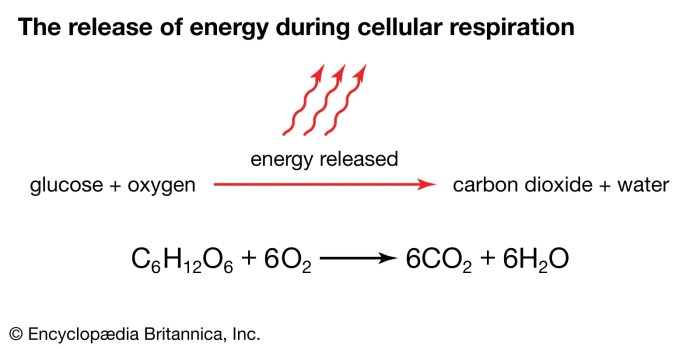
Combustion Reactions
Combustion reactions are a type of chemical reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen, releasing heat and light. The general equation for a combustion reaction is:
Fuel + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Heat
For example, when methane (CH 4) burns in air, it reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide (CO 2), water (H 2O), and heat.
Question Bank: Types Of Chemical Reactions Packet
What are the main types of chemical reactions?
The primary types of chemical reactions include synthesis, decomposition, single-replacement, double-replacement, and combustion reactions.
How are chemical reactions classified?
Chemical reactions can be classified based on various criteria, such as energy changes (exothermic or endothermic), the nature of the reactants (ionic or covalent), and the type of products formed (acid-base or redox reactions).
What is the significance of balancing chemical equations?
Balancing chemical equations ensures that the number of atoms of each element is conserved on both sides of the equation, providing an accurate representation of the reaction stoichiometry and facilitating quantitative analysis.