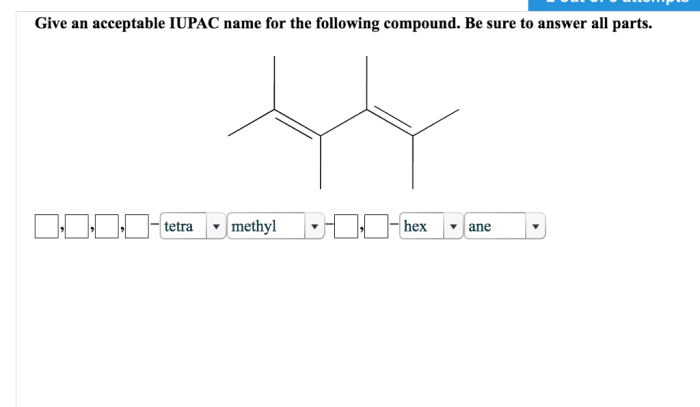
Give an acceptable IUPAC name for the following compound. This question delves into the fascinating realm of IUPAC nomenclature, a system that provides a standardized language for naming organic compounds. Understanding IUPAC nomenclature is crucial for chemists to communicate clearly and accurately about the structures and properties of these molecules.
IUPAC nomenclature follows a set of well-defined rules that assign systematic names to organic compounds based on their structural features. These names provide essential information about the compound’s structure, including the number and type of carbon atoms, the presence of functional groups, and the arrangement of substituents.
By adhering to IUPAC guidelines, chemists can ensure that the names they assign to compounds are unambiguous and universally recognized.
Introduction
IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic method of naming chemical compounds that is used by chemists worldwide. It was developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and is based on a set of rules that ensure that compounds are named in a consistent and unambiguous manner.
IUPAC nomenclature is important because it allows chemists to communicate about chemical compounds clearly and concisely. It also helps chemists to identify and classify compounds, and to predict their properties and reactivity.
Examples of IUPAC Names for Simple Compounds
- Methane (CH 4)
- Ethane (C 2H 6)
- Propane (C 3H 8)
- Butane (C 4H 10)
- Pentane (C 5H 12)
Rules for Naming Organic Compounds
Naming Alkanes
- The base name of an alkane is derived from the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
- The suffix “-ane” is added to the base name.
- The carbon atoms in the molecule are numbered from one end to the other.
- The location of any substituents is indicated by a number.
Naming Alkenes
- The base name of an alkene is derived from the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
- The suffix “-ene” is added to the base name.
- The location of the double bond is indicated by a number.
Naming Alkynes
- The base name of an alkyne is derived from the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
- The suffix “-yne” is added to the base name.
- The location of the triple bond is indicated by a number.
Functional Groups
Functional groups are groups of atoms that have characteristic chemical properties. They are used to classify organic compounds and to predict their reactivity.
Common Functional Groups
- Alcohols (-OH)
- Aldehydes (-CHO)
- Ketones (-CO-)
- Carboxylic acids (-COOH)
Naming Compounds Containing Multiple Functional Groups
- The functional group with the highest priority is named first.
- The other functional groups are named in order of decreasing priority.
- The prefixes “di-“, “tri-“, and “tetra-” are used to indicate the number of functional groups present.
Complex Organic Compounds
Complex organic compounds are molecules that contain a large number of atoms and functional groups. They can be difficult to name using the basic rules of IUPAC nomenclature.
Naming Heterocycles
- Heterocycles are cyclic compounds that contain one or more atoms other than carbon.
- The base name of a heterocycle is derived from the number of atoms in the ring and the type of heteroatom(s) present.
- The suffix “-ine” is added to the base name.
Naming Polycyclic Compounds
- Polycyclic compounds are molecules that contain two or more rings.
- The base name of a polycyclic compound is derived from the number of rings and the type of rings present.
- The suffix “-ane” is added to the base name.
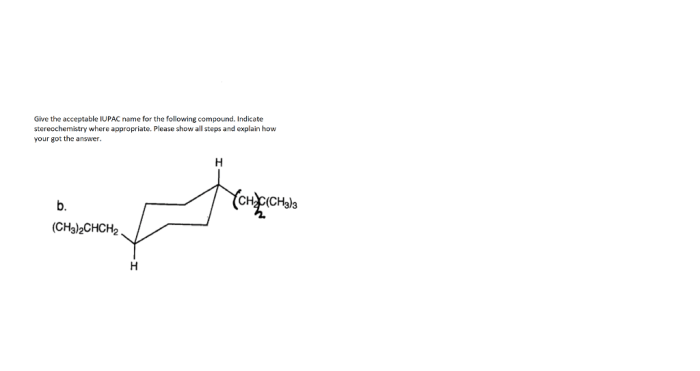
Stereochemistry: Give An Acceptable Iupac Name For The Following Compound.
Stereochemistry is the study of the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in molecules. It is important in IUPAC nomenclature because it allows chemists to distinguish between compounds that have the same molecular formula but different spatial arrangements.
Types of Stereoisomers
- Enantiomers are molecules that are mirror images of each other.
- Diastereomers are molecules that are not mirror images of each other but have the same molecular formula.
- Meso compounds are molecules that have a plane of symmetry and are not optically active.
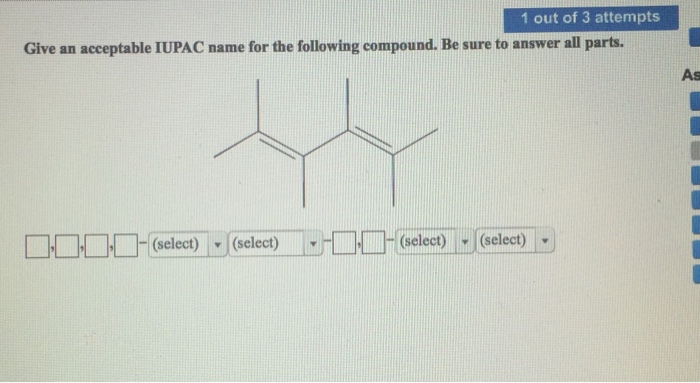
Naming Stereoisomers, Give an acceptable iupac name for the following compound.
- Enantiomers are named using the prefixes “R” and “S”.
- Diastereomers are named using the prefixes “cis” and “trans”.
- Meso compounds are named using the prefix “meso”.
FAQ Overview
What is the purpose of IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature provides a standardized system for naming organic compounds, ensuring clear and unambiguous communication among chemists.
How does IUPAC nomenclature assign names to compounds?
IUPAC nomenclature uses a set of rules to assign systematic names based on the compound’s structure, including the number and type of carbon atoms, the presence of functional groups, and the arrangement of substituents.
Why is it important to use IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature promotes consistency and clarity in chemical communication, facilitating collaboration, research, and the advancement of chemistry.