Streptomyces differs from Actinomyces because Streptomyces possesses distinctive characteristics that set it apart as a unique genus. This article delves into the defining features of Streptomyces bacteria, exploring their morphology, ecological niches, and significance in antibiotic production and industrial applications.
By contrasting Streptomyces with Actinomyces, we gain a deeper understanding of the diversity and complexity within the bacterial world.
Streptomyces, renowned for its prolific production of bioactive compounds, has played a pivotal role in the discovery and development of antibiotics. Its industrial applications extend beyond medicine, encompassing biotechnology, bioremediation, and environmental cleanup. As we unravel the intricate differences between Streptomyces and Actinomyces, we uncover the remarkable adaptations and capabilities of these fascinating microorganisms.
Characteristics of Streptomyces
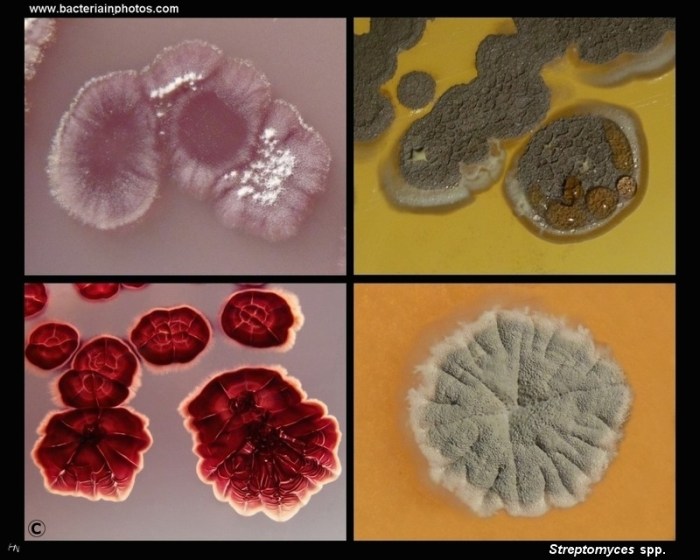
Streptomyces are Gram-positive, aerobic bacteria belonging to the Actinomycetes class. They are characterized by their filamentous morphology, forming branching mycelia. Individual cells are rod-shaped, with a diameter of 0.5-1.5 μm and a length of 1-10 μm. Streptomyces are non-motile and have a complex cell wall composition, containing peptidoglycan, teichoic acids, and mycolic acids.
Streptomyces Habitat and Distribution
Streptomyces are ubiquitous in nature, found in various habitats, including soil, water, and decaying organic matter. They are particularly abundant in soil, where they play crucial roles in nutrient cycling and decomposition. Streptomyces are distributed worldwide, with different species adapted to diverse environmental conditions.
Streptomyces and Antibiotic Production

Streptomyces bacteria are renowned for their ability to produce a wide range of antibiotics. These bioactive compounds are essential in combating bacterial infections. Streptomyces produce antibiotics through complex biosynthetic pathways, often involving multiple enzymes and genes. Antibiotics produced by Streptomyces include streptomycin, erythromycin, and tetracycline, which have played a significant role in treating various infectious diseases.
Streptomyces Industrial Applications: Streptomyces Differs From Actinomyces Because Streptomyces
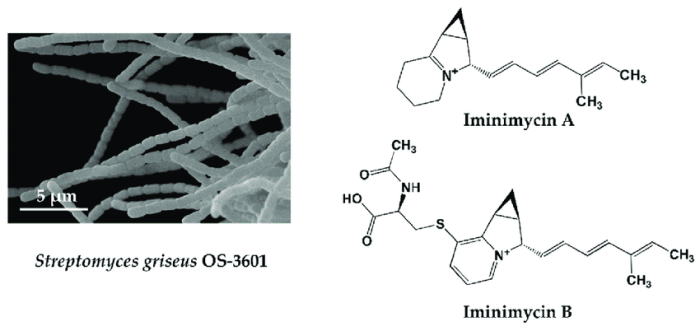
Beyond antibiotic production, Streptomyces bacteria have various industrial applications. They are used in biotechnology for enzyme production, such as proteases, amylases, and lipases. Streptomyces are also employed in fermentation processes for the production of vitamins, amino acids, and other valuable compounds.
Additionally, they have potential applications in bioremediation, where they can degrade environmental pollutants and contribute to environmental cleanup.
Streptomyces Differentiation from Actinomyces
Streptomyces and Actinomyces are closely related bacteria, both belonging to the Actinomycetes class. However, they can be differentiated based on several key characteristics. Streptomyces form aerial hyphae that develop into chains of spores, while Actinomyces lack aerial hyphae and produce spores within sporangia.
Additionally, Streptomyces have a higher guanine-cytosine (GC) content in their DNA compared to Actinomyces.
User Queries
What are the main morphological differences between Streptomyces and Actinomyces?
Streptomyces exhibits a filamentous growth pattern, forming branched hyphae that can extend over long distances. In contrast, Actinomyces typically forms shorter, unbranched hyphae.
How does Streptomyces contribute to antibiotic discovery?
Streptomyces is a prolific producer of bioactive compounds, including many antibiotics. These compounds have revolutionized the treatment of infectious diseases and saved countless lives.
What are some industrial applications of Streptomyces?
Streptomyces is used in biotechnology for the production of enzymes and other valuable compounds. It also has potential applications in bioremediation and environmental cleanup.