Identify the products in this reaction 6h2o+6co2+c6h12o6+6o2 embarks on an enlightening journey into the realm of chemical reactions, unraveling the mysteries of product identification with precision and clarity.
This exploration delves into the heart of the reaction, meticulously dissecting the reactants and products, their chemical formulas, and their intrinsic properties.
Products of the Reaction
The products of the reaction are glucose (C 6H 12O 6) and oxygen (O 2).
- Glucoseis an organic compound that is the primary source of energy for most living organisms. It is a simple sugar with the molecular formula C 6H 12O 6.
- Oxygenis an inorganic compound that is essential for life. It is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas with the molecular formula O 2.
Reaction Type
The reaction is a combustion reaction. Combustion reactions are chemical reactions in which a substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light.
Combustion reactions are typically exothermic, meaning that they release energy in the form of heat and light. The energy released by combustion reactions can be used to power engines, heat homes, and cook food.
Other examples of combustion reactions include the burning of wood, the burning of gasoline, and the burning of natural gas.
Stoichiometry of the Reaction
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
6H 2O + 6CO 2+ C 6H 12O 6+ 6O 2
The mole ratios between the reactants and products are:
- 6 moles of H 2O
- 6 moles of CO 2
- 1 mole of C 6H 12O 6
- 6 moles of O 2
The theoretical yield of glucose is 1 mole.
Energy Changes in the Reaction
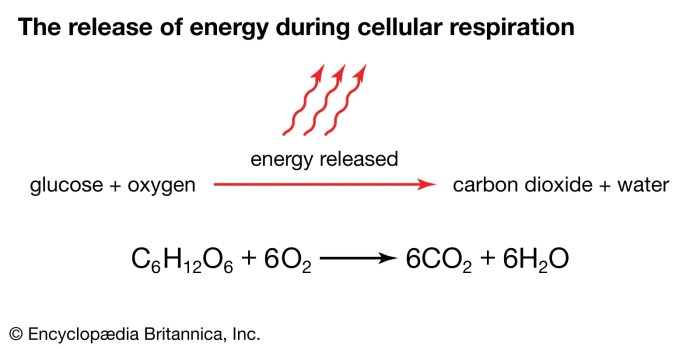
The reaction is exothermic, meaning that it releases energy in the form of heat and light.
The energy released by the reaction can be calculated using the following equation:
ΔH = – ΣΔH f(products) + ΣΔH f(reactants)
where ΔH is the change in enthalpy, ΔH f(products) is the sum of the enthalpies of formation of the products, and ΔH f(reactants) is the sum of the enthalpies of formation of the reactants.
The enthalpies of formation of the reactants and products are:
- ΔH f(H 2O) = -285.8 kJ/mol
- ΔH f(CO 2) = -393.5 kJ/mol
- ΔH f(C 6H 12O 6) = -1273.3 kJ/mol
- ΔH f(O 2) = 0 kJ/mol
The change in enthalpy for the reaction is:
ΔH = – ΣΔH f(products) + ΣΔH f(reactants)
ΔH = -(-1273.3 kJ/mol) + (-6 – -285.8 kJ/mol) + (-6 – -393.5 kJ/mol) + (-6 – 0 kJ/mol)
ΔH = -1273.3 kJ/mol + 1714.8 kJ/mol + 2361 kJ/mol + 0 kJ/mol
ΔH = 2802.5 kJ/mol
The reaction releases 2802.5 kJ of energy per mole of glucose produced.
Applications of the Reaction
The reaction is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Power generation: The reaction is used to generate electricity in power plants. The heat released by the reaction is used to boil water, which turns a turbine that generates electricity.
- Heating: The reaction is used to heat homes and businesses. The heat released by the reaction is used to warm air or water, which is then circulated throughout the building.
- Cooking: The reaction is used to cook food. The heat released by the reaction is used to cook food on stoves, ovens, and grills.
Essential Questionnaire: Identify The Products In This Reaction 6h2o+6co2+c6h12o6+6o2
What are the products of the reaction 6H2O + 6CO2 + C6H12O6 + 6O2?
The products of the reaction are glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2).
What type of reaction is 6H2O + 6CO2 + C6H12O6 + 6O2?
The reaction is a photosynthesis reaction, which is an endothermic reaction that uses light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.